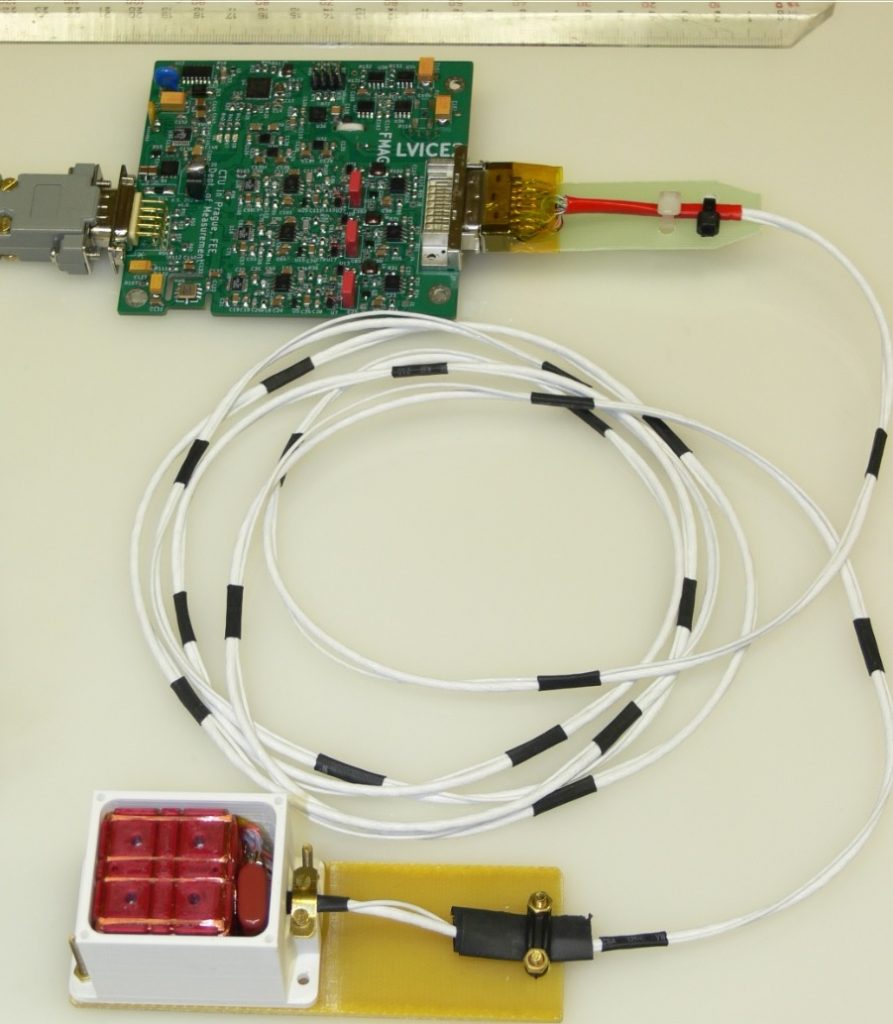
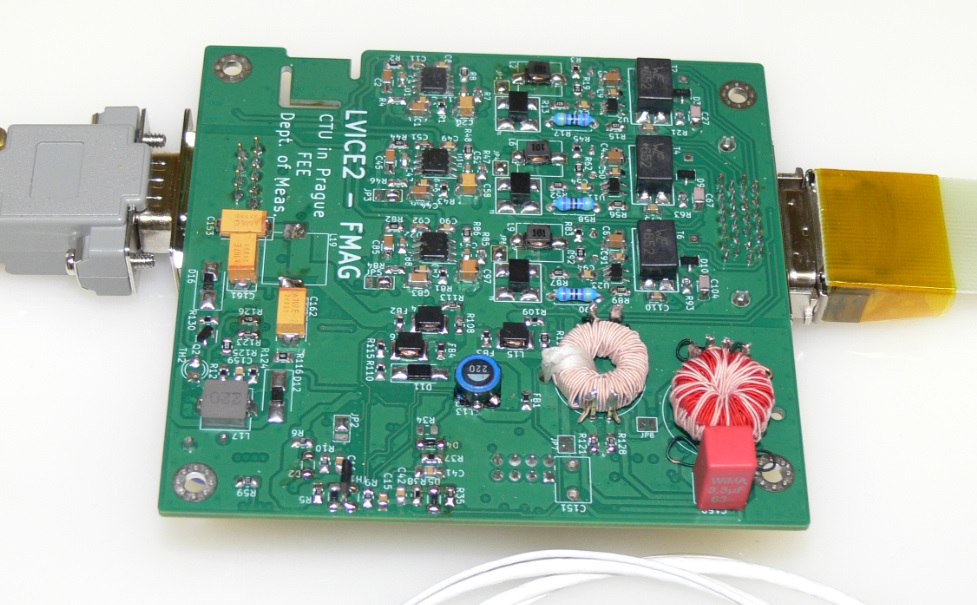
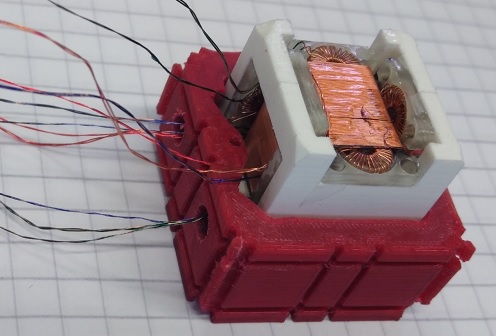
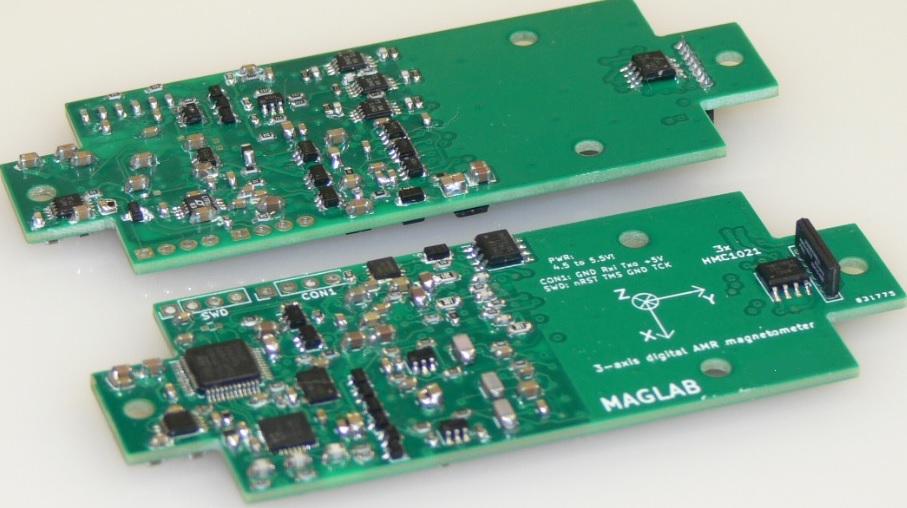
Since June 2022 we work on LVICE2 – Lunar VIcinity Complex Environmental Explorer – mission to visit near-Moon space and gather some interesting data there. MAGLAB is responsible for development and delivery of two magnetometers. The first one, fluxgate sensor based, will be used to study plasma and solar wind turbulences. The second, AMR based magnetometer with lower resolution will be located within the satellite body and help to remove possible magnetic disturbances caused by the satellite itself from the fluxgate magnetometer data.
First prototype of the fluxgate magnetometer has been developed during the winter semester of 2022, manufactured and tested in the scope of bachelor thesis by Kajetán Šobíšek (Cybernetics and Robotics study branch), supervised by Vojtěch Petrucha who also developed and built the fluxgate sensor itself (using partially 3D printed components to speed-up the process). David Novotný is working on the AMR magnetometer (reduced full-scale range, interfaces…). During the summer semester of 2023 we will construct a test platform to evaluate the de-noising algorithm, hopefully conduct a first radiation testing of the fluxgate magnetometer (AMR magnetometer has been already successfully tested to withstand up to 50 krad TID of 60Co gamma rays). Plus of course huge amount of paperwork is in front of us…
Please keep the fingers crossed for successful selection of the project during July 2023, where the winner of the Czech ambitious mission call should be chosen.